The Bitcoin network's upcoming halving in March 2028 will unfold in the most institutionally mature environment in cryptocurrency history, with - over 10% of Bitcoin's supply now controlled by corporations and ETFs - compared to less than 1% during the 2020 halving.
This fundamental shift from retail-driven to institution-dominated ownership, combined with comprehensive regulatory frameworks and technical infrastructure that didn't exist in previous cycles, suggests the 2028 halving will operate as a supply shock amplifier rather than a speculative catalyst. While historical halvings generated 93x to 7x price multipliers, the 2028 event faces a transformed landscape where - 1.4 million bitcoins sit in ETF vaults - and corporate treasuries hold another - 855,000 bitcoins - , creating structural demand that could sustain price appreciation even as percentage gains moderate from previous cycles.
The mathematics remain unchanged: mining rewards will drop from 3.125 to 1.5625 bitcoins per block, reducing daily supply from 450 to 225 new bitcoins when approximately - 1.275 million bitcoins remain unmined - . However, the economic context has revolutionized. BlackRock's Bitcoin ETF alone commands - $71 billion in assets - , while MicroStrategy holds - 582,000 bitcoins - worth over $62 billion.
This institutional presence provides both price stability buffers and sustained demand pressure that previous halvings lacked, creating conditions where supply reduction meets structurally altered demand patterns in ways that could extend typical cycle timelines while supporting higher price floors.
The scarcity mathematics driving bitcoin's digital gold thesis
Bitcoin's monetary policy operates with mathematical precision unmatched by any asset in human history. As of August 2025, - 19.725 million bitcoins have been mined - , representing 94% of the protocol's hard-coded maximum supply of 21 million coins. This leaves merely - 1.275 million bitcoins remaining - to be discovered through mining operations that will continue until approximately 2140, when the final satoshis enter circulation. The exponential supply curve means that over 87% of total bitcoins were mined by 2020, with the remaining 13% requiring over a century to complete due to the halving mechanism's geometric progression.
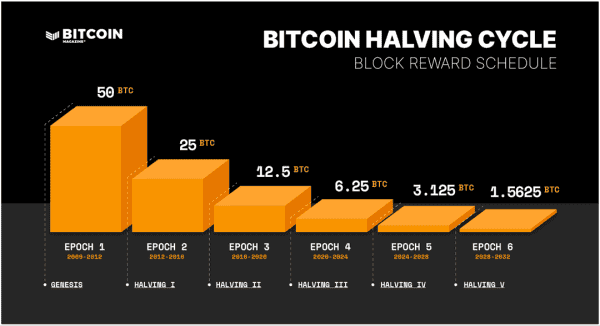
Every 210,000 blocks, roughly every four years, the protocol automatically reduces mining rewards by half without any human intervention or governance decisions. The progression follows an elegant mathematical sequence: 50 bitcoins per block from 2009 to 2012, then 25 bitcoins until 2016, followed by 12.5 bitcoins through 2020, and 6.25 bitcoins from 2020 to April 2024. The current reward of - 3.125 bitcoins per block - will persist until March 2028, when the fifth halving reduces new supply to 1.5625 bitcoins per block.
This halving mechanism creates a stock-to-flow ratio that currently exceeds silver and approaches gold's scarcity metrics. The ratio measures existing supply against new annual production, with Bitcoin's current stock-to-flow around 58 expected to double to approximately 116 after the 2028 halving. Gold maintains a stock-to-flow ratio near 70, while industrial commodities typically range from 1 to 5, making Bitcoin increasingly scarce relative to traditional stores of value.
The energy economics underlying this scarcity have evolved dramatically. Modern ASIC miners consume approximately - 854,404 kilowatt-hours per bitcoin - mined post-halving, nearly double the pre-halving energy requirement. This energy intensification, combined with hash rate growth to - 898.86 exahashes per second - , demonstrates how market forces maintain network security even as rewards diminish. Mining difficulty adjusts every 2,016 blocks to maintain the ten-minute average block time, ensuring supply predictability regardless of computational power fluctuations.
Network participants understand that approximately - 3-4 million bitcoins are permanently lost - due to forgotten private keys, destroyed hardware, and inaccessible wallets, reducing the effective circulating supply to perhaps 16-17 million bitcoins. This reality amplifies scarcity beyond the protocol's mathematical limits, as lost coins create deflationary pressure that no central authority can reverse through money printing or asset seizure.
How institutional adoption rewrote the halving playbook
The transformation from retail-dominated to institution-led Bitcoin ownership represents the most significant structural change since the network's creation. During the 2020 halving, institutional ownership barely registered as a meaningful market force. Today, - BlackRock's IBIT ETF alone holds over $71 billion in bitcoin assets - , while the collective ETF ecosystem controls - 1.4 million bitcoins - representing 6.8% of total supply. Corporate treasuries add another - 855,000 bitcoins - to institutional holdings, bringing total institutional ownership above 10% of circulating supply.
MicroStrategy leads corporate adoption with - 582,000 bitcoins - valued at over $62 billion, executing a treasury strategy that has inspired dozens of public companies to allocate capital to Bitcoin. The company targets $84 billion in total Bitcoin purchases by 2027 and has already completed 32% of this ambitious accumulation program. Marathon Digital, Bitcoin Standard Treasury, and other public companies hold substantial positions, while GameStop raised $1.5 billion specifically for Bitcoin treasury allocation through its "Project Rocket" initiative.
This institutional accumulation has fundamentally altered supply dynamics heading into the 2028 halving. Exchange reserves have declined to - 2.5 million bitcoins - , the lowest levels since 2019, as institutional buyers withdraw coins to secure custody solutions. The withdrawal of - 425,000 bitcoins from exchanges - since November 2024 coincided with - 350,000 bitcoins acquired by publicly traded companies - during the same period, demonstrating how institutional demand directly reduces liquid trading supply.
Goldman Sachs exemplifies traditional finance's Bitcoin evolution, increasing its Bitcoin ETF position by 88% to become BlackRock's largest IBIT shareholder with - $1.4 billion in holdings - . JPMorgan holds nearly $1 billion in Bitcoin ETFs while launching cryptocurrency services for Chase credit card customers. Morgan Stanley, Charles Schwab, and PNC Bank have announced Bitcoin integration plans, while State Street develops comprehensive custody infrastructure for institutional clients.
The ETF ecosystem's maturation addresses institutional requirements that previous halving cycles couldn't meet. In-kind creation and redemption mechanisms launched in July 2025 improve ETF efficiency and reduce tracking errors. The - $40 billion weekly trading volume - achieved by Bitcoin and Ethereum ETFs in August 2025 demonstrates institutional-grade liquidity that rivals traditional asset classes. This infrastructure provides institutions with regulated exposure to Bitcoin's upside without operational complexities of direct ownership.
Corporate treasury adoption follows different dynamics than ETF investment. Companies like MicroStrategy view Bitcoin as superior treasury assets to cash or bonds, making strategic allocation decisions based on long-term value storage rather than short-term trading. This creates "strong hands" ownership that historically maintains positions through market volatility, providing price support during corrections and reducing selling pressure during bull markets.
The mining industry's transformation through four halving cycles
Bitcoin mining has evolved from bedroom hobby to industrial operation through four halving events, each requiring technological and economic adaptation to maintain profitability with reduced rewards. The network's hash rate progression tells this story quantitatively: from negligible computational power in 2009 to - 898.86 exahashes per second - today, representing more computing power than most countries possess. This exponential growth occurred despite mining rewards dropping from 50 bitcoins per block to the current 3.125 bitcoins, demonstrating how Bitcoin price appreciation and technological advancement offset halving impacts.
The current mining landscape features publicly traded companies operating at unprecedented scale. Marathon Digital maintains - 29.9 exahashes per second - of operational capacity across multiple data centers, targeting 50 exahashes by year-end through continued expansion. Core Scientific operates - 19.1-20.1 exahashes per second - of self-mining capacity while diversifying into AI and high-performance computing hosting services. Riot Platforms, CleanSpark, TeraWulf, and other major operators collectively control significant portions of global hash rate, representing a consolidation trend that accelerated after each halving as less efficient miners exited the market.
Mining pool distribution reflects geographic and technological shifts since Bitcoin's early years. Foundry USA leads with - 33.49% of global hash rate - , representing a shift toward North American mining infrastructure. AntPool maintains - 18.24% - despite Chinese regulatory restrictions that forced geographic redistribution. The United States now hosts over - 40% of global hash rate - , up from negligible levels during earlier halving cycles, while China's dominance has declined dramatically from historical peaks above 75%.
Technological efficiency improvements have been crucial for mining profitability across halving cycles. Modern ASIC miners achieve - 24-26 joules per terahash - , compared to early equipment consuming hundreds of joules per terahash. Next-generation miners target - 5 joules per terahash - by 2025, representing a 3x efficiency improvement that could offset halving impact on marginal mining operations. This efficiency race drives constant capital investment in newer equipment, with older miners becoming unprofitable as rewards decline.
Energy consumption patterns have shifted toward renewable sources as mining operations seek cost advantages and regulatory compliance. Cambridge University data indicates Bitcoin mining now uses - 43% renewable energy - , including hydro, wind, solar, and nuclear power. Mining companies increasingly co-locate with renewable energy projects, providing demand for stranded energy resources that would otherwise go unutilized. Texas leads this trend, with mining operations balancing wind and solar intermittency while participating in grid stabilization services.
The economic reality facing miners heading into 2028 involves doubled production costs due to halving effects. Current mining operations become profitable at electricity costs below - $0.06 per kilowatt-hour - for older equipment, while next-generation miners extend profitability thresholds to higher energy costs. Post-halving, these thresholds effectively double, forcing industry consolidation among the most efficient operators with access to cheapest electricity sources.
Mining revenue increasingly depends on transaction fees as block rewards diminish over successive halvings. Currently, transaction fees represent a small fraction of total mining revenue, but fee markets become increasingly important for long-term network security. During network congestion periods, daily fees can exceed $3 million, compared to historical averages below $1 million. The development of fee markets becomes critical for maintaining mining incentives beyond 2140 when block rewards reach zero.
Geographic distribution continues evolving due to regulatory changes and energy economics. While China's mining ban forced massive relocations, countries like Kazakhstan, Russia, and Canada have attracted significant mining investment. The United States benefits from diverse energy markets, favorable regulations in states like Texas and Wyoming, and established financial infrastructure supporting publicly traded mining companies. This geographic diversification reduces regulatory risks while improving network decentralization.
Historical halving impacts reveal evolving market patterns
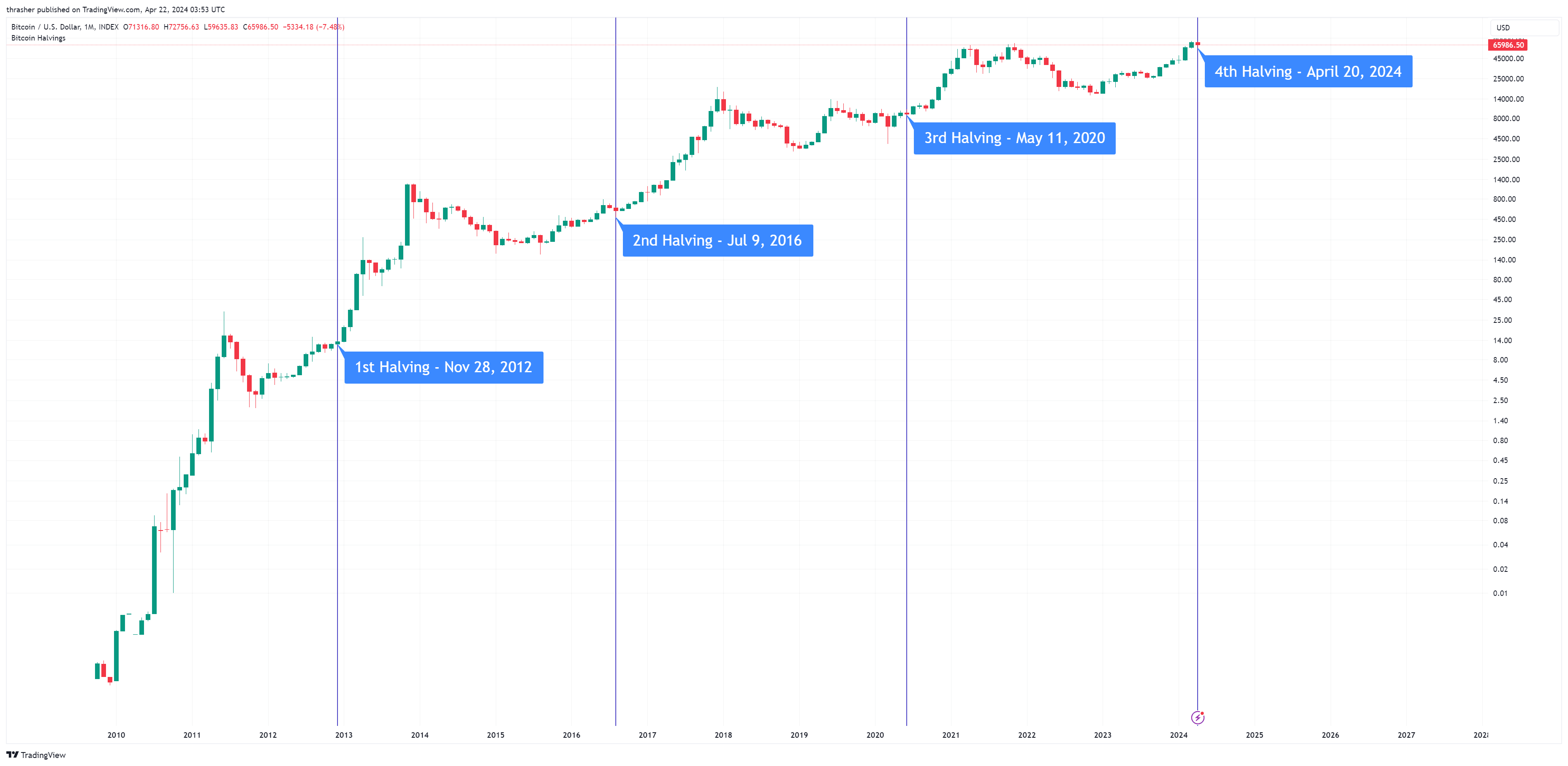
Bitcoin's four completed halvings provide quantitative evidence for how supply reductions affect price discovery, though each cycle occurred within different market contexts that influenced magnitude and timing of price responses. The mathematical progression shows diminishing returns as Bitcoin matures, but also longer cycle durations and higher absolute price levels that maintain mining profitability despite reduced percentage gains.
The November 28, 2012 halving established the foundational pattern when mining rewards dropped from 50 to 25 bitcoins per block. Bitcoin traded at - $12.35 on halving day - and reached - $1,147 within twelve months - , representing a staggering 9,188% gain. This inaugural halving cycle occurred during Bitcoin's experimental phase with minimal institutional awareness, limited exchange infrastructure, and CPU-based mining operations. The network's hash rate barely exceeded 25 terahashes per second, while daily trading volumes remained below $10 million.
The July 9, 2016 halving reduced rewards from 25 to 12.5 bitcoins per block amid growing institutional interest and professional mining operations. Bitcoin's halving day price of - $650.63 - preceded an initial 40% decline before the sustained bull market drove prices to - $19,987 by December 2017 - , a 2,972% gain over seventeen months. This cycle featured the emergence of cryptocurrency derivatives, regulated exchanges, and ASIC mining equipment that dramatically increased network security to 1.5 exahashes per second.
The May 11, 2020 halving coincided with COVID-19 pandemic uncertainty and early institutional adoption signals. MicroStrategy and Tesla's corporate treasury allocations during this cycle marked the beginning of institutional acceptance. Bitcoin's halving day price of - $8,821 - eventually reached - $69,040 by November 2021 - , representing a 683% gain over eighteen months. The concurrent DeFi boom and NFT speculation created additional demand for Bitcoin as a foundational cryptocurrency, while network hash rate expanded to 120 exahashes per second.
The April 20, 2024 halving broke historical patterns by occurring after Bitcoin had already achieved new all-time highs in March 2024. The - $73,135 pre-halving peak - represented the first time Bitcoin reached record prices before a halving event, driven by ETF launches that generated over $9 billion in institutional inflows. Bitcoin traded at - $64,968 on halving day - before declining 16% in subsequent weeks, suggesting traditional "sell-the-news" dynamics as the event became widely anticipated.
Academic analysis reveals consistent statistical patterns across halvings despite different market contexts. Regression analysis demonstrates 95% confidence intervals for outperformance beginning 100+ days post-halving, with optimal timing windows occurring 400-720 days after each event. The average performance 500 days post-halving across the first three cycles exceeded 1,800% gains, though with decreasing magnitude as Bitcoin's market capitalization expanded.
Mathematical models based on historical data predict the next cycle peak around November 2025, approximately 19 months after the 2024 halving. These models anticipate the following trough in November 2026, 31 months post-halving, based on extending historical cycle patterns. However, the unprecedented pre-halving all-time high and institutional demand structure suggest traditional timing models may require recalibration for current market conditions.
The evolution from 93x gains in 2012 to 7x gains in 2020 demonstrates Bitcoin's maturation trajectory while absolute price increases remain substantial. Even diminished percentage returns translate to significant dollar appreciation as Bitcoin's price base expands. A theoretical 3x gain from $70,000 pre-2028 halving levels would reach $210,000, representing hundreds of billions in market capitalization increase despite modest percentage terms relative to early cycles.
Market microstructure has transformed across halving cycles as institutional participation increased. The 2012 cycle featured retail-dominated trading with high individual volatility. The 2016 cycle included early institutional players alongside sophisticated retail traders. The 2020 cycle mixed retail enthusiasm with emerging corporate adoption. The 2024 cycle demonstrated institutional flows dominating through ETF demand structure, creating different volatility patterns and recovery timelines compared to retail-driven historical cycles.
Corporate treasuries and ETFs reshape demand dynamics
The structural transformation of Bitcoin demand from speculative trading to strategic allocation fundamentally alters traditional halving economics. Unlike retail investors who often trade based on sentiment and technical analysis, institutional holders typically maintain positions through extended periods, creating sustained demand pressure that previous cycles lacked. This "strong hands" ownership pattern becomes increasingly significant as institutional allocation percentages continue expanding.
BlackRock's IBIT ETF exemplifies institutional demand mechanics with - $71 billion in assets under management - and record-breaking inflows reaching - $6.35 billion in May 2025 alone - . The fund's success demonstrates institutional appetite for Bitcoin exposure through regulated financial products rather than direct cryptocurrency ownership. IBIT's - $4.2 billion single-day trading volume - in April 2025 exceeded many individual stock trading volumes, indicating Bitcoin's integration into traditional portfolio management strategies.
The competitive dynamic between ETFs and corporate treasury adoption reveals different institutional approaches to Bitcoin investment. While ETFs provide diversified exposure for institutional investors managing multiple asset classes, corporate treasury allocation represents strategic decisions by individual companies to hold Bitcoin as a primary reserve asset. The second quarter of 2025 data shows - corporate treasuries acquired 131,000 bitcoins - compared to - 111,000 bitcoins added by ETFs - , marking the third consecutive quarter where direct corporate buying exceeded ETF accumulation.
MicroStrategy's treasury strategy serves as a template for corporate Bitcoin adoption, with the company holding - 582,000 bitcoins - valued at over $62 billion. The company's aggressive acquisition program targets $84 billion in total Bitcoin purchases by 2027, representing one of the largest corporate asset allocation strategies in history. MicroStrategy's approach involves using debt and equity offerings specifically to fund Bitcoin purchases, creating a direct pipeline from capital markets to Bitcoin demand.
The withdrawal of - 425,000 bitcoins from exchanges - since November 2024 demonstrates how institutional accumulation directly impacts liquid supply. This phenomenon creates artificial scarcity beyond the protocol's halving mechanism, as long-term holders remove coins from trading circulation. Exchange reserves at - 2.5 million bitcoins - represent five-year lows, indicating that available supply for trading has declined even as total bitcoins in circulation continue growing through mining.
Goldman Sachs's evolution exemplifies traditional finance's Bitcoin integration path. The investment bank increased its Bitcoin ETF holdings by - 88% to $1.4 billion - , becoming BlackRock's largest IBIT shareholder while expanding cryptocurrency services for institutional clients. This progression from skepticism to significant allocation reflects broader Wall Street acceptance that began during the 2020 halving cycle and accelerated through ETF approvals in 2024.
The regulatory framework supporting institutional adoption has matured significantly since previous halvings. SEC approval of spot Bitcoin ETFs in January 2024 removed regulatory barriers that previously limited institutional participation. The subsequent approval of in-kind creation and redemption mechanisms in July 2025 improved ETF efficiency and reduced tracking errors that concerned sophisticated investors. These regulatory improvements create operational infrastructure supporting sustained institutional demand through the 2028 halving cycle.
Banking sector integration accelerates institutional adoption through traditional financial service channels. JPMorgan's partnership with Coinbase enables Chase credit card cryptocurrency funding, while PNC Bank offers direct crypto trading through bank accounts. Morgan Stanley considers Bitcoin ETF recommendations to thousands of brokers, potentially exposing millions of retail investors to Bitcoin through traditional wealth management relationships.
The transformation from trading-focused to holding-focused demand patterns suggests different price behavior around the 2028 halving. Historical cycles featured rapid price appreciation followed by significant corrections as retail traders took profits. Institutional holders typically maintain positions through volatility periods, focusing on long-term value appreciation rather than short-term trading gains. This behavioral difference could extend bull market durations while moderating peak-to-trough volatility that characterized previous cycles.
Mining economics evolution through industrial transformation
Bitcoin mining has transformed from decentralized individual activity to consolidated industrial operations through successive halving cycles, with major implications for network security, geographic distribution, and economic sustainability heading into 2028. The mathematical reality that mining rewards halve every four years while operational costs continue rising has forced constant technological innovation and operational efficiency improvements to maintain profitability margins.
The current hash rate of - 898.86 exahashes per second - represents computational power that exceeds most nations' combined processing capacity, securing Bitcoin's network through proof-of-work consensus. This hash rate has grown despite three consecutive halvings, demonstrating how Bitcoin price appreciation and technological advancement have offset reward reductions. However, the upcoming 2028 halving will test this dynamic as rewards drop from 3.125 to 1.5625 bitcoins per block, effectively doubling production costs for marginal mining operations.
Modern ASIC miners achieve efficiency levels of - 24-26 joules per terahash - , representing thousand-fold improvements from early mining equipment. Companies like Bitmain, MicroBT, and Canaan continue advancing semiconductor design to maintain competitive advantages as halvings reduce profit margins. Next-generation miners targeting - 5 joules per terahash - by 2025 could provide 3x efficiency improvements that partially offset halving impacts, though technological improvement rates have decelerated from the exponential gains achieved in Bitcoin's early years.
Publicly traded mining companies now dominate hash rate distribution, replacing the individual miners who secured the network during early halvings. Marathon Digital's - 29.9 exahashes per second - operational capacity requires industrial-scale infrastructure across multiple data centers with aggregate power consumption exceeding small cities. Core Scientific operates - 19.1-20.1 exahashes per second - while diversifying into AI and high-performance computing hosting to optimize facility utilization and revenue streams beyond Bitcoin mining.
The geographic redistribution following China's mining ban demonstrates how regulatory changes can rapidly reshape network security distribution. Chinese mining operations that once controlled over 75% of global hash rate relocated to Kazakhstan, Russia, Canada, and the United States within months of the 2021 restrictions. The United States now hosts over - 40% of global hash rate - , benefiting from diverse energy markets, favorable regulations in states like Texas and Wyoming, and established financial infrastructure supporting publicly traded mining companies.
Energy sourcing has become a critical competitive advantage as mining operations seek lowest-cost electricity to maintain profitability margins. Cambridge University data indicates - 43% renewable energy usage - including hydro, wind, solar, and nuclear power sources. Texas leads renewable mining development, with operations balancing wind and solar intermittency while providing grid stabilization services during peak demand periods. Mining companies increasingly co-locate with renewable energy projects, monetizing stranded energy resources that lack transmission infrastructure to reach traditional demand centers.
The economic threshold for mining profitability centers on electricity costs, with current operations requiring sub-$0.06 per kilowatt-hour rates for older equipment to remain viable. Post-2028 halving, these thresholds will effectively double, forcing industry consolidation among operators with access to the cheapest energy sources and most efficient equipment. This consolidation trend has accelerated after each halving as less efficient miners exit the market, leaving operations with sustainable competitive advantages.
Transaction fee revenue becomes increasingly important for long-term mining sustainability as block rewards approach zero through successive halvings. Current daily transaction fees average - $3 million during congestion periods - compared to historical levels below $1 million, representing growing fee market development. However, fees still constitute a small fraction of total mining revenue compared to block rewards, creating long-term questions about network security funding beyond 2140 when rewards reach zero.
Mining pool distribution reflects the consolidation of hash rate among major operators. Foundry USA controls - 33.49% of global hash rate - , primarily serving North American mining companies with professional-grade pool services. AntPool maintains - 18.24% - despite regulatory restrictions on Chinese mining operations. The concentration of hash rate among top pools raises decentralization concerns, though pool participants can switch operators if pools behave maliciously, providing economic incentives for fair operation.
The development of dual-use mining infrastructure represents an emerging trend where facilities optimize utilization across cryptocurrency mining and alternative computing workloads like AI training and high-performance computing. This diversification strategy helps mining companies maintain facility utilization during periods when Bitcoin mining becomes temporarily unprofitable, providing revenue stability through commodity price cycles.
Environmental regulations increasingly influence mining operations as governments implement carbon emission restrictions and renewable energy requirements. The European Union recommends eliminating tax incentives for cryptocurrency miners, while various jurisdictions implement direct restrictions on fossil fuel-powered mining operations. These regulatory trends favor mining companies with renewable energy sources and carbon-neutral operations, creating competitive advantages beyond pure electricity cost considerations.
Price forecasting models and analyst predictions converge on substantial appreciation
The convergence of quantitative models, institutional analysis, and academic research suggests significant Bitcoin price appreciation through the 2028 halving cycle, though predictions vary substantially in magnitude and timeline. Traditional financial institutions, cryptocurrency research firms, and academic models generally agree on upward price trajectories while differing on specific targets and methodological approaches to valuation.
ARK Invest presents the most aggressive institutional predictions with - bear case targets around $300,000 - , - base case scenarios near $710,000 - , and - bull case projections reaching $1.5 million by 2030 - . Their multi-factor model incorporates institutional ETF adoption rates, emerging market demand patterns, potential nation-state reserves, and Metcalfe's Law network effects to justify exponential growth trajectories. The model assumes Bitcoin ETFs will represent 15% of total supply by 2033, requiring sustained institutional accumulation that extends current adoption trends.
Traditional investment banks provide more conservative but still bullish assessments based on production cost analysis and store-of-value competition models. Goldman Sachs projects Bitcoin could reach - $100,000 by capturing 20% of the global store-of-value market - , competing directly with gold's traditional safe-haven role. JPMorgan's production cost models suggest mining economics support prices above - $53,000 - post-halving, though the bank initially projected corrections before sustained appreciation.
Stock-to-flow models, despite criticism following 2022 divergences, continue projecting substantial appreciation based on scarcity metrics. The current stock-to-flow ratio near 58 is expected to double to approximately 116 after the 2028 halving, supporting price targets above - $130,000 - based on historical correlations. While the model failed during the 2022 crypto winter, proponents argue that institutional adoption and regulatory clarity create different market dynamics that could restore historical relationships between scarcity and price.
Metcalfe's Law applications to Bitcoin valuation suggest exponential growth potential based on network expansion. Fidelity's models predict - $1 billion per Bitcoin by 2038-2040 - with intermediate targets near - $1 million by 2030 - based on user adoption curves and network value relationships. These models assume continued expansion of Bitcoin's user base and utility beyond pure speculation toward functional money and store-of-value applications.
Academic research provides mixed perspectives on Bitcoin's long-term valuation potential. Federal Reserve analysis notes Bitcoin's disconnection from traditional macroeconomic factors, questioning whether standard asset pricing models apply to cryptocurrency markets. However, network externality research suggests value increases proportionally with adoption and transaction volume, supporting bullish long-term trajectories if Bitcoin achieves broader acceptance as digital money.
Risk scenario analysis reveals substantial uncertainty around central predictions despite general bullish consensus. Regulatory crackdowns, technical failures, market saturation, rising interest rates making yield-bearing assets more attractive, and mining centralization concerns could derail appreciation trajectories. Conversely, nation-state Bitcoin reserves, accelerated institutional adoption, monetary debasement driving alternative asset demand, and successful Layer 2 development could exceed even aggressive price targets.
Monte Carlo simulations attempt to quantify prediction uncertainty through probabilistic modeling. ARK Invest's analysis suggests - 77% probability of positive returns - with 95% confidence intervals ranging from - $30,000 to $448,000 - for one-year projections, demonstrating substantial uncertainty despite bullish central tendencies. These wide prediction ranges reflect genuine uncertainty about adoption rates, regulatory responses, and macroeconomic conditions affecting Bitcoin's trajectory.
Production cost models focus on mining economics to establish price floors, arguing that Bitcoin prices tend to approximate marginal production costs over extended periods. Post-2028 halving, production costs effectively double as rewards decline, potentially supporting higher sustainable price levels. However, these models assume continued mining profitability and ignore potential efficiency improvements that could reduce costs.
Comparative analysis with traditional commodities provides additional valuation frameworks. Bitcoin's stock-to-flow ratio approaching gold levels suggests potential price parity or premium based on superior portability, divisibility, and verifiability characteristics. If Bitcoin captures significant market share from gold's - $13 trillion market capitalization - , individual Bitcoin prices could reach hundreds of thousands of dollars based purely on market substitution effects.
The consensus among credible analysts centers on substantial appreciation through the 2028 halving cycle, with conservative estimates projecting - $100,000-$200,000 price levels - and aggressive models suggesting - $400,000-$600,000 targets - . The wide range reflects genuine uncertainty about institutional adoption rates, regulatory responses, technological developments, and macroeconomic conditions that will ultimately determine Bitcoin's price trajectory through the next halving cycle.
Regulatory environment transformation creates unprecedented institutional support
The regulatory landscape surrounding Bitcoin has undergone fundamental transformation since previous halving cycles, evolving from hostile skepticism to structured acceptance that provides institutional investors with legal clarity and operational frameworks necessary for large-scale adoption. This regulatory evolution creates a dramatically different environment for the 2028 halving compared to previous cycles that occurred amid regulatory uncertainty and enforcement actions.
The Trump administration's January 23, 2025 executive order "Strengthening American Leadership in Digital Financial Technology" represents the most comprehensive pro-cryptocurrency policy framework in U.S. history. The order establishes goals to make America the "crypto capital of the world" while promoting dollar-backed stablecoins and creating a Strategic Bitcoin Reserve and Digital Asset Stockpile. This policy reversal from the previous administration's enforcement-heavy approach provides regulatory certainty that institutional investors require for strategic allocations.
SEC transformation under Chairman Paul Atkins replaced Gary Gensler's confrontational regulatory approach with innovation-focused frameworks designed to provide clear pathways for cryptocurrency businesses. The crypto task force led by Commissioner Hester Peirce develops comprehensive regulations covering securities classification, tailored disclosure frameworks, and realistic registration pathways. This collaborative approach contrasts sharply with the enforcement actions and regulatory uncertainty that characterized previous halving cycles.
The rescission of SAB 121 removes major barriers preventing banks from offering cryptocurrency custody services without onerous balance sheet requirements. This regulatory change enables traditional financial institutions to provide Bitcoin custody and trading services directly, expanding institutional access beyond specialized cryptocurrency service providers. Major banks including JPMorgan, Goldman Sachs, and Morgan Stanley have announced cryptocurrency service expansions following this regulatory clarity.
Bitcoin ETF approvals in January 2024 marked a watershed moment for institutional acceptance, providing regulated investment vehicles that meet fiduciary standards required by pension funds, endowments, and institutional investment managers. The subsequent approval of in-kind creation and redemption mechanisms in July 2025 improved ETF efficiency and reduced tracking errors that concerned sophisticated investors. These regulatory approvals created operational infrastructure supporting over - $500 billion in Bitcoin ETF assets under management - as of 2025.
State-level Bitcoin adoption accelerates through legislative initiatives supporting cryptocurrency reserves and payments. New Hampshire allocates 5% of state reserves to Bitcoin, while Arizona launches Bitcoin reserve programs. These state-level adoptions create regulatory precedents and political momentum for broader governmental acceptance, potentially influencing federal policy development and international regulatory coordination efforts.
International regulatory coordination through G20 and Financial Action Task Force (FATF) standards implementation creates global frameworks for cryptocurrency compliance and cross-border transactions. The Common Reporting Framework for Crypto-Assets (CARF) enables automatic exchange of cryptocurrency transaction information among 48 countries beginning in 2025, providing tax authorities with comprehensive data while creating regulatory certainty for institutional investors operating across multiple jurisdictions.
The European Union's Markets in Crypto-Assets (MiCA) regulation achieved full implementation across all member states by December 30, 2024, providing comprehensive frameworks for crypto-asset service providers and stablecoin regulations. EU-wide passporting rights enable authorized cryptocurrency services to operate across all member states, creating regulatory efficiency and market access that supports institutional adoption throughout Europe.
Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC) developments paradoxically support Bitcoin demand through competitive dynamics. While 137 countries representing 98% of global GDP explore CBDCs, research indicates these government digital currencies have positive correlation with Bitcoin returns. The Trump administration's prohibition on U.S. CBDCs while promoting dollar-backed stablecoins creates policy clarity that benefits Bitcoin as a non-government digital asset alternative.
Tax treatment evolution provides institutional investors with operational certainty required for strategic allocations. Form 1099-DA reporting requirements beginning in 2025 create comprehensive cryptocurrency transaction reporting, while cost basis tracking requirements starting in 2026 provide accounting clarity for institutional portfolio management. These regulatory developments eliminate tax ambiguity that previously complicated institutional Bitcoin adoption.
Environmental regulations increasingly influence mining operations through carbon emission restrictions and renewable energy requirements, though regulatory approaches vary significantly by jurisdiction. The EU recommends eliminating tax incentives for cryptocurrency miners, while U.S. states like Texas provide incentives for renewable energy mining projects. This regulatory fragmentation creates competitive advantages for jurisdictions with favorable cryptocurrency policies while potentially restricting mining in environmentally conscious regions.
Banking integration accelerates through regulatory clarity enabling traditional financial institutions to offer cryptocurrency services. JPMorgan's partnership with Coinbase for Chase credit card cryptocurrency funding, PNC Bank's direct crypto trading through bank accounts, and Morgan Stanley's consideration of Bitcoin ETF recommendations demonstrate how regulatory certainty enables traditional finance integration with cryptocurrency markets.
The contrast with previous halving cycles demonstrates regulatory evolution's significance for institutional adoption. The 2012 halving occurred amid complete regulatory uncertainty, with Mt. Gox serving as the primary exchange without meaningful oversight. The 2016 halving featured early regulatory frameworks but continued enforcement uncertainty. The 2020 halving included growing regulatory clarity but limited institutional infrastructure. The 2028 halving will occur within comprehensive regulatory frameworks supporting institutional participation at unprecedented scale.
Technical network developments expand bitcoin's utility beyond digital gold
Bitcoin's technical infrastructure has evolved substantially through Layer 2 solutions, protocol improvements, and scaling developments that expand the network's utility beyond simple value storage, creating additional demand drivers that could amplify the 2028 halving's economic impact. These technical developments address historical limitations around transaction throughput, programmability, and user experience while maintaining Bitcoin's base layer security and decentralization properties.
The Lightning Network represents the most significant Layer 2 scaling solution, with - $145 million in total value locked - across - 16,400 nodes - and - 75,700 payment channels - as of 2025. Lightning enables instant Bitcoin transactions with average costs of - 0.0016 satoshis ($0.000000443) - , dramatically reducing fees compared to base layer transactions that can exceed $10 during network congestion. This payment infrastructure creates utility for Bitcoin as medium of exchange rather than purely store of value, potentially expanding demand beyond speculative and treasury allocation use cases.
Lightning Network adoption accelerates through merchant integration, remittance services, and micropayment applications that leverage Bitcoin's programmable money characteristics. Major payment processors including Strike, Cash App, and various international remittance services utilize Lightning for cross-border transfers that bypass traditional correspondent banking systems. These use cases create sustained demand for Bitcoin liquidity while demonstrating practical applications that extend beyond speculative investment.
Rootstock (RSK) provides smart contract functionality with Ethereum compatibility while maintaining Bitcoin's security through merge-mining. This sidechain enables decentralized finance applications, tokenization projects, and programmable Bitcoin functionality that competing blockchains have dominated. RSK's development creates potential for Bitcoin to capture value from decentralized finance markets without compromising the base layer's conservative development approach.
Stacks represents another major Layer 2 development enabling smart contracts and decentralized applications on Bitcoin through its unique consensus mechanism that settles transactions to Bitcoin's base layer. Stacks' programming language Clarity provides formal verification capabilities that enhance security compared to other smart contract platforms, while Bitcoin anchoring ensures transaction finality through proof-of-work consensus.
Liquid Network operates as a federated sidechain providing faster settlement times and enhanced privacy features for institutional Bitcoin transactions. The network facilitates high-volume trading and custody operations through major exchanges and financial institutions, creating infrastructure that supports institutional adoption while reducing base layer congestion from large-value transfers.
State channel implementations beyond Lightning Network provide additional scaling solutions for specific use cases including gaming, micropayments, and streaming applications. These technical developments create programmable Bitcoin functionality without compromising base layer security, enabling new applications that generate sustained demand for Bitcoin liquidity.
Bitcoin Improvement Proposal (BIP) process continues advancing protocol development through community consensus, with - 389 BIPs - in Bitcoin's history addressing consensus-critical changes, protocol improvements, and process enhancements. Recent BIPs focus on privacy improvements, scaling optimizations, and developer tooling that enhance Bitcoin's technical capabilities while maintaining backward compatibility and decentralization properties.
Taproot activation in 2021 provided the foundation for enhanced privacy and programmability that Layer 2 solutions continue building upon. Taproot's script efficiency improvements reduce transaction costs and enable more complex smart contract functionality while maintaining privacy through output indistinguishability. These base layer improvements support Layer 2 development and expand Bitcoin's technical capabilities.
Mining infrastructure developments include stranded energy monetization, renewable energy integration, and dual-use facilities that optimize computational resources across cryptocurrency mining and artificial intelligence workloads. These infrastructure improvements enhance mining economics while addressing environmental concerns that could influence regulatory responses and institutional adoption decisions.
The development of Bitcoin-native financial services creates additional demand for Bitcoin beyond speculative trading and treasury allocation. Lending protocols, derivatives platforms, and custody services built on Bitcoin infrastructure enable sophisticated financial applications while maintaining Bitcoin's security properties. These services create yield generation opportunities that compete with traditional fixed-income investments.
Privacy enhancements through Lightning Network, coin mixing services, and protocol developments address institutional concerns about transaction visibility and regulatory compliance. Enhanced privacy features enable Bitcoin usage in applications requiring confidential transactions while maintaining regulatory transparency through selective disclosure mechanisms.
Cross-chain interoperability solutions enable Bitcoin integration with other blockchain networks through wrapped Bitcoin tokens, atomic swaps, and bridge protocols. These technical developments expand Bitcoin's utility across decentralized finance ecosystems while maintaining native Bitcoin ownership and security properties.
Technical infrastructure maturation creates sustained demand drivers beyond speculative investment that could amplify the 2028 halving's economic impact. As Bitcoin evolves from digital gold to programmable money through Layer 2 solutions, the network captures value from payments, decentralized finance, and various applications that generate consistent demand for Bitcoin liquidity. This utility expansion creates additional upward pressure on Bitcoin prices that compounds with supply reduction effects from the halving mechanism.
Comparison with traditional commodities reveals bitcoin's unique economic properties
Bitcoin's monetary and economic characteristics diverge substantially from traditional commodities, creating unique supply-demand dynamics that may amplify halving effects beyond historical commodity market behavior. While gold and other precious metals provide useful comparison frameworks, Bitcoin's digital nature, programmatic scarcity, and network effects generate economic properties without precedent in traditional commodity markets.
Gold maintains a stock-to-flow ratio near 70 through approximately 3,000 tonnes of annual production against existing above-ground stocks of roughly 200,000 tonnes. Bitcoin's current stock-to-flow ratio of 58 approaches gold's scarcity level and will exceed it after the 2028 halving when the ratio reaches approximately 116. However, Bitcoin's supply schedule operates through algorithmic certainty rather than geological discovery and mining economics that influence gold production, creating fundamentally different supply dynamics.
Unlike gold mining that responds to price incentives through increased exploration and production capacity, Bitcoin mining cannot increase supply above the predetermined issuance schedule regardless of price levels or mining investment. This supply inelasticity means Bitcoin price appreciation cannot trigger supply responses that moderate price increases, as occurs with traditional commodities during bull markets. The mathematical certainty of Bitcoin's supply schedule creates scarcity economics without precedent in commodity markets.
Industrial commodities like copper, oil, and agricultural products typically maintain stock-to-flow ratios between 1 and 5, reflecting their consumption in manufacturing and energy production. These commodities experience supply-demand balancing through production adjustments and substitute goods that moderate price extremes. Bitcoin's lack of industrial consumption or substitute goods creates demand dynamics driven purely by monetary and speculative factors rather than productive economic applications.
Silver provides interesting comparison as both industrial metal and monetary asset, with a stock-to-flow ratio around 25 that Bitcoin has already exceeded. Silver's dual demand from industrial applications and investment creates different price dynamics compared to pure store-of-value assets like Bitcoin. However, silver's supply responds to mining economics and recycling that can moderate price appreciation, while Bitcoin's fixed supply schedule prevents supply-side responses to demand increases.
Traditional commodity trading involves physical storage, transportation, quality verification, and delivery mechanisms that create operational costs and market frictions. Bitcoin's digital nature eliminates these physical constraints while enabling instant global transfer, divisibility to eight decimal places, and perfect authenticity verification through cryptographic signatures. These superior monetary properties create competitive advantages over physical commodities for store-of-value applications.
Network effects distinguish Bitcoin from traditional commodities through Metcalfe's Law relationships where network value increases proportionally to the square of user adoption. Gold and other commodities lack network effects, with their value determined purely by supply-demand balancing rather than network expansion. Bitcoin's network effects create potential for exponential value appreciation as adoption increases, contrasting with linear supply-demand relationships governing traditional commodities.
Storage and custody differences create operational advantages for Bitcoin compared to physical commodities. Gold storage requires secure vaults, insurance, transportation, and verification systems that generate ongoing costs and operational risks. Bitcoin storage requires secure key management but eliminates physical infrastructure costs while enabling global accessibility through internet connectivity. These operational advantages reduce barriers to Bitcoin ownership and accumulation.
Divisibility and transferability provide Bitcoin with monetary properties that exceed traditional commodities. Gold's physical properties limit divisibility and complicate small-value transactions, while Bitcoin enables micro-transactions and precise value transfer without physical constraints. These properties support Bitcoin's utility as medium of exchange in addition to store-of-value applications, creating broader demand patterns than pure commodity investments.
Market structure differences affect price discovery mechanisms between Bitcoin and traditional commodities. Commodity markets feature established futures markets, spot trading, and industrial hedging that create sophisticated price discovery mechanisms. Bitcoin markets remain relatively nascent but increasingly sophisticated through ETF development, derivatives markets, and institutional participation that improve price efficiency and reduce volatility.
Regulatory frameworks governing Bitcoin differ substantially from traditional commodity regulations developed over decades of market evolution. Commodity markets operate under comprehensive regulatory oversight addressing market manipulation, position limits, and delivery requirements. Bitcoin regulation continues evolving but increasingly resembles securities regulation rather than commodity frameworks, creating different market dynamics and investor protection mechanisms.
The absence of productive yield distinguishes Bitcoin from income-generating assets but aligns with gold and other non-yielding stores of value. However, Bitcoin's potential for yield generation through lending, staking derivatives, and Layer 2 applications creates opportunities for return enhancement without compromising base asset ownership, contrasting with physical commodities that lack similar yield opportunities.
Correlation patterns between Bitcoin and traditional commodities reveal changing relationships as Bitcoin matures. Early Bitcoin development showed minimal correlation with commodity markets, but institutional adoption has increased correlation with risk assets while maintaining negative correlation with the U.S. dollar. These correlation patterns suggest Bitcoin increasingly functions as risk asset rather than commodity hedge, though this relationship may evolve as institutional adoption progresses.
The unique combination of programmatic scarcity, network effects, superior monetary properties, and institutional adoption creates economic dynamics for Bitcoin that differ fundamentally from traditional commodities. While commodity frameworks provide useful analytical tools, Bitcoin's digital nature and network characteristics generate unprecedented economic behavior that may amplify halving effects beyond historical commodity market patterns.
Current 2025 market conditions set stage for unprecedented halving dynamics
The Bitcoin market environment heading into the 2028 halving presents unprecedented institutional adoption, regulatory clarity, and technical infrastructure that fundamentally differs from conditions surrounding previous halving events. These structural changes suggest the 2028 halving will operate within mature financial markets rather than speculative cryptocurrency ecosystems that characterized earlier cycles, potentially creating different risk-reward profiles and volatility patterns.
Institutional ownership concentration has reached levels that create structural demand and supply dynamics unlike previous halving cycles. With - over 10% of Bitcoin supply controlled by institutions - through ETFs and corporate treasuries, the market features significant "strong hands" ownership that historically maintains positions through volatility periods. This ownership concentration reduces liquid trading supply while providing price support during market corrections, creating conditions where supply reduction from halving meets already constrained available supply.
Bitcoin's correlation with traditional financial markets has evolved from near-zero relationships during early halvings to current correlations of - 0.58 with the Russell 1000 - and - 0.53 with financial stocks - . This integration with traditional markets means Bitcoin price movements increasingly reflect broader economic conditions, institutional portfolio allocation decisions, and macroeconomic factors rather than purely cryptocurrency-specific developments. These correlation patterns suggest the 2028 halving will occur within broader financial market context rather than isolated cryptocurrency speculation.
The emergence of Bitcoin as a treasury asset for public companies creates sustained demand that operates independently of speculative trading cycles. MicroStrategy's - 582,000 bitcoin holdings - and aggressive acquisition program targeting - $84 billion in total purchases by 2027 - represents strategic allocation decisions based on long-term value storage rather than short-term trading. This corporate treasury trend creates predictable demand that could provide price floors during market volatility.
Current trading volumes averaging - $38.9 billion daily - demonstrate institutional-grade liquidity that supports large-value transactions without significant price impact. However, exchange reserves at - 2.5 million bitcoins - representing five-year lows indicate that available trading supply has declined even as institutional participation has increased. This combination of high liquidity and reduced available supply creates market conditions where incremental demand could generate substantial price impacts.
The regulatory environment provides institutional investors with legal clarity and operational frameworks that enable strategic Bitcoin allocation decisions. SEC approval of Bitcoin ETFs, banking integration through traditional financial institutions, and comprehensive regulatory frameworks remove barriers that previously limited institutional participation. This regulatory clarity enables pension funds, endowments, and other fiduciary investors to consider Bitcoin allocation without previous legal uncertainties.
Interest rate environment and monetary policy create macroeconomic conditions that could influence Bitcoin demand through the 2028 halving cycle. Federal Reserve policy decisions, inflation expectations, and currency debasement concerns affect institutional asset allocation decisions between Bitcoin, bonds, equities, and alternative investments. Bitcoin's negative correlation with the U.S. dollar creates potential hedging demand during currency weakness periods.
Geopolitical developments including nation-state Bitcoin adoption, central bank digital currency competition, and international monetary system evolution create additional demand drivers beyond traditional investment allocation. Countries like El Salvador's Bitcoin legal tender adoption and proposed U.S. Strategic Bitcoin Reserve create government demand that operates independently of market speculation, potentially providing sustained price support through halving cycles.
Technical infrastructure maturation through Layer 2 solutions, payment systems, and financial services creates utility demand for Bitcoin beyond speculative investment and treasury allocation. Lightning Network growth, decentralized finance integration, and merchant acceptance create sustained demand for Bitcoin liquidity that compounds with investment demand to create upward price pressure.
Market microstructure evolution toward institutional-grade trading infrastructure supports large-value transactions and sophisticated trading strategies that improve price discovery and reduce manipulation risks. Professional market makers, algorithmic trading systems, and derivatives markets create trading environments that resemble traditional asset markets rather than early cryptocurrency exchanges with limited liquidity and operational risks.
The unprecedented combination of institutional ownership, regulatory clarity, technical infrastructure, and macroeconomic conditions creates market conditions for the 2028 halving that differ fundamentally from previous cycles. These structural changes suggest potential for sustained price appreciation with reduced volatility compared to retail-driven historical cycles, though absolute price movements may remain substantial due to Bitcoin's expanding market capitalization and institutional demand patterns.
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations increasingly influence institutional Bitcoin allocation decisions through renewable energy mining requirements, carbon accounting frameworks, and sustainability reporting standards. Mining industry evolution toward renewable energy sources and carbon-neutral operations addresses institutional concerns while creating operational advantages for mining companies with environmental compliance.
Derivatives market development provides institutional investors with sophisticated risk management tools including futures, options, and structured products that enable hedged Bitcoin exposure and yield generation strategies. These financial instruments create additional demand for underlying Bitcoin while providing institutions with familiar risk management frameworks from traditional asset classes.
Long-term implications beyond the 2028 halving
The 2028 Bitcoin halving represents a pivotal transition point in cryptocurrency evolution from experimental technology to established institutional asset class, with long-term implications extending far beyond immediate price impacts. The convergence of institutional adoption, regulatory frameworks, technical infrastructure, and global monetary uncertainty creates conditions that could establish Bitcoin's role in the international financial system for decades following the halving event.
Monetary policy implications become increasingly significant as Bitcoin's stock-to-flow ratio exceeds gold and central banks grapple with debt sustainability and currency debasement concerns. Bitcoin's fixed supply schedule provides institutional investors and nation-states with hedging mechanisms against monetary expansion that traditional assets cannot match. The mathematical certainty of Bitcoin's scarcity creates competitive advantages over gold and other stores of value that depend on mining economics and geological constraints.
The transition from mining reward dependence to transaction fee sustainability approaches critical thresholds as successive halvings reduce block rewards toward zero. Post-2028, mining rewards of 1.5625 bitcoins per block will require substantial fee market development to maintain network security through economic incentives. Layer 2 solutions and increased Bitcoin utility could generate sufficient transaction volume and fees to sustain mining operations, though this transition remains untested at required scales.
International monetary system integration could accelerate through nation-state Bitcoin adoption and central bank reserve diversification. Countries facing currency instability, sanctions risks, or inflation pressures may increase Bitcoin allocation as shown by El Salvador's legal tender adoption and proposed U.S. Strategic Bitcoin Reserve legislation. This government demand creates sustained upward price pressure while establishing Bitcoin as geopolitical asset alongside gold and foreign exchange reserves.
Financial infrastructure maturation through traditional banking integration, custody solutions, and regulatory frameworks enables Bitcoin participation by pension funds, insurance companies, and sovereign wealth funds with trillion-dollar asset bases. These institutional investors operate with longer time horizons and larger capital bases than current Bitcoin holders, potentially creating sustained demand that extends through multiple halving cycles.
Technology evolution through quantum computing, cryptographic advances, and blockchain scaling solutions could affect Bitcoin's long-term value proposition and network security. While quantum computing threatens current cryptographic security, Bitcoin's development community has already begun preparing quantum-resistant solutions. Successful adaptation to technological challenges could reinforce Bitcoin's antifragile characteristics and institutional confidence.
Competitive landscape development through central bank digital currencies, alternative cryptocurrencies, and traditional financial innovation creates potential challenges to Bitcoin's monetary role. However, Bitcoin's decentralized architecture, proven track record, and network effects provide competitive advantages that government-controlled digital currencies cannot replicate. Competition could accelerate Bitcoin innovation while validating its core value propositions.
Environmental sustainability requirements increasingly influence institutional Bitcoin allocation decisions through ESG investment frameworks and regulatory compliance standards. Mining industry evolution toward renewable energy sources and carbon-neutral operations addresses these concerns while creating operational advantages for environmentally compliant miners. Successful environmental integration could eliminate barriers to institutional adoption while supporting long-term price appreciation.
Generational wealth transfer represents significant long-term demand driver as younger demographics with cryptocurrency familiarity inherit substantial wealth from traditional asset holders. This demographic transition could accelerate Bitcoin adoption as portfolio allocation preferences shift toward digital assets, creating sustained demand that extends beyond current institutional adoption trends.
The mathematical progression toward Bitcoin's 21 million maximum supply creates increasingly rare events as remaining bitcoins decline toward zero over the next century. Each subsequent halving reduces available new supply by smaller absolute amounts but maintains percentage reductions, creating potential for sustained scarcity premiums that could extend price appreciation across multiple decades.
Economic theory development around digital scarcity, network effects, and programmable money continues evolving as Bitcoin demonstrates unprecedented monetary properties. Academic research, central bank analysis, and institutional frameworks increasingly recognize Bitcoin's unique characteristics while developing analytical tools and valuation models specific to digital assets rather than traditional commodity frameworks.
The intersection of artificial intelligence, blockchain technology, and digital payments could create novel applications for Bitcoin that extend utility beyond current store-of-value and payment functions. These technological convergences may generate demand drivers that amplify network effects while creating new economic models around programmable money and autonomous financial systems.
Global financial system resilience benefits from Bitcoin's decentralized architecture that operates independently of traditional banking infrastructure, government monetary policy, and geopolitical conflicts. These systemic advantages become increasingly valuable during financial crises, banking failures, or international conflicts that compromise traditional financial systems, potentially creating sustained demand for decentralized alternatives.
Conclusion: the institutional halving era
The 2028 Bitcoin halving will mark the definitive transition from Bitcoin's experimental phase to its institutional epoch, fundamentally altering the economic dynamics that have characterized previous supply reduction events. The convergence of unprecedented institutional ownership exceeding 10% of total supply, comprehensive regulatory frameworks, and mature financial infrastructure creates conditions where traditional halving effects may be both amplified through constrained liquidity and moderated through sophisticated market participation.
Unlike previous cycles driven by retail speculation and technical adoption, the 2028 halving occurs within an environment where - 1.4 million bitcoins sit in ETF vaults - , - 582,000 bitcoins anchor MicroStrategy's treasury strategy - , and traditional financial institutions integrate Bitcoin services across their client bases. This institutional presence provides both sustained demand drivers and price stability mechanisms that previous cycles lacked, suggesting potential for extended appreciation periods with reduced volatility amplitude characteristic of mature asset classes.
The mathematical certainty of mining reward reduction from 3.125 to 1.5625 bitcoins per block creates predictable supply constraints that will interact with structurally altered demand patterns in unprecedented ways. With exchange reserves at five-year lows of 2.5 million bitcoins and institutional accumulation continuing to remove coins from liquid trading supply, the 2028 halving's supply shock will operate within already constrained market conditions that could amplify traditional scarcity effects.
Technical infrastructure evolution through Layer 2 solutions, payment systems, and financial applications expands Bitcoin's utility beyond pure speculation or treasury allocation, creating sustained demand for Bitcoin liquidity that compounds with investment demand. Lightning Network growth, smart contract capabilities, and traditional finance integration demonstrate Bitcoin's evolution toward programmable money that captures value from diverse economic applications rather than purely speculative trading.
The regulatory transformation from enforcement uncertainty to structured acceptance provides institutional investors with legal clarity and operational frameworks necessary for strategic allocations. SEC Bitcoin ETF approvals, banking integration authorization, and comprehensive compliance standards remove barriers that previously limited institutional participation while creating infrastructure supporting trillion-dollar asset class development.
Price forecasting convergence among credible institutional analysts suggests substantial appreciation potential through the 2028 halving cycle, with conservative estimates projecting $100,000-$200,000 levels and aggressive models reaching $400,000-$600,000 targets. These predictions reflect genuine institutional adoption trends and supply-demand economics rather than speculative enthusiasm, indicating sustainable appreciation potential supported by fundamental economic drivers.
The broader implications extend beyond immediate price impacts toward Bitcoin's role in international monetary systems, portfolio allocation strategies, and technological innovation across financial services. The 2028 halving represents not merely another supply reduction event but a confirmation of Bitcoin's transition from experimental technology to established monetary asset that competes directly with gold, government bonds, and traditional stores of value.
Most significantly, the 2028 halving will test whether Bitcoin's institutional maturation maintains the network effects and appreciation potential that characterized earlier cycles or whether market efficiency and institutional sophistication moderate historical patterns toward more traditional asset behavior. The unprecedented combination of mathematical scarcity, institutional adoption, and regulatory integration creates conditions for Bitcoin's most significant economic experiment since its creation - demonstrating whether digital scarcity can maintain exponential growth characteristics within mature financial systems.
This institutional halving era marks Bitcoin's graduation from cryptocurrency markets to traditional asset class inclusion, with implications for monetary policy, portfolio theory, and international finance that will extend far beyond the immediate supply reduction effects. The 2028 halving stands as the definitive test of Bitcoin's ability to maintain revolutionary growth characteristics while achieving evolutionary integration within established financial systems.

